Near-field-scanner
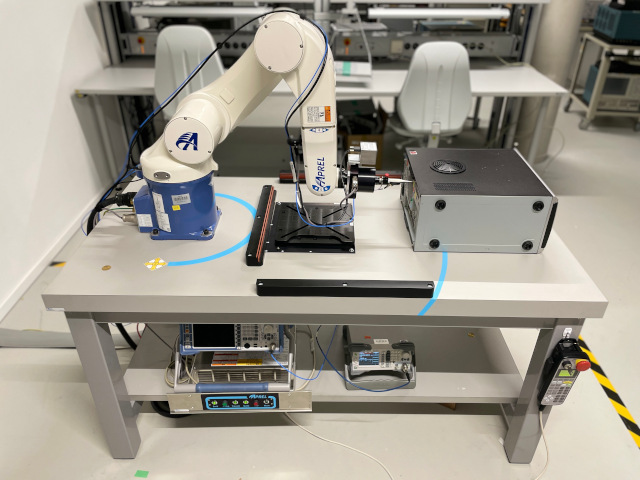
- Near-field measurement 9 kHz to 6 GHz and far-field approximation
- Six-axis robot (X/Y/Z + 360 degree rotation)
- Step resolution and repeatability < 50 um
- Miniaturized E-/H-field probe (tip size < 2 mm)
- Measurable volume (75cm x 75cm x 60cm)
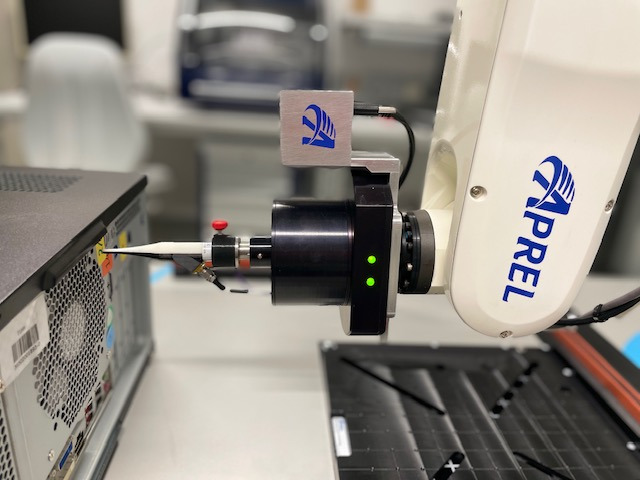

- Safe surface and collision detection
- Universal server for remote control
- TCP/IP LAN bus for communication and control
- Image acquisition, control and calibration
The near-field scanner is the ideal measuring device that can measure electric or magnetic fields from a few kHz up to 6 GHz in detail in the near-field. Thereby an exact image in 2-D or 3-D of the entire field distribution on a device under test (DUT) can be created, and compared with electromagnetic simulations by e.g. CONCEPT-II. The robotic arm-guided near-field probe is used to electrically scan individual measurement points with high spatial precision. The measured objects are printed circuit boards equipped with components, models in development, as well as small antenna structures. Electrical functions of circuits – especially on small test structures – are better understood and faults are easier to locate because individual and extremely small noise sources are faster to locate and identify on the DUT. With a regular grid and discrete points, the spatial dimensions of the DUT are fast identified. With the setup of the parameters the six-axis robot arm is enabled to perform the electromagnetic simulations automatically. The currents from the measurement device are available and processed in the robot software for each measurement position. The recorded measured values of the near-field probe and the connected measurement devices are stored together as a near-field scan. After completion of all scans of the DUT the entire near-field scan is immediately displayed with all measurement data in a comprehensive result log. All required measuring devices have to be connected to the robot system ready for operation. All safety settings must be checked for proper function on the control unit of the robot system. After log in at the control software, the near-field probe must first be calibrated. With a safe distance to the robot arm and with the help of the calibration software, the probe is carefully placed on the calibration measuring point (calibration beacon) of the work table plate by means of the hand-held control unit. The robot arm can be finely controlled with a reduced speed. After calibration the robot moves back to is standby position automatically. Further calibration can be performed with a software-known field (reference microstrip printed circuit board) for investigations of scattering parameters and immunity and susceptibility tests. First measurement positions on the DUT are performed in manual mode with the hand-held control unit. The Computer program is used to enter the necessary start settings, format settings, the selection of H-field and E-field measurements, and the necessary measurement parameters. The robot scans all calculated positions full automatically. The robot system is equipped with extensive safety features including detection and protective shutdowns of axial and radial collisions with the probe. For safety reasons, no person is allowed to be near the robot or in the EMC laboratory while the robot is in automatic mode.
