Thermo-Electrical EMC Filter Design for Electric Vehicles (TEFDEV)

Funding: Valeo eAutomotive Germany GmbH
Contact: Lennart Bohl, M. Sc.
Start date: 01.10.2023

In the powertrain of electric cars, high demands are placed on the inverters that generate the three-phase AC voltage for the electric motor from the battery’s DC voltage. They must be small, light, inexpensive and efficient. Additionally, the trend in the electric car industry is towards higher power, voltage and switching frequency. This results in high electrical and thermal loads on all components within the powertrain as well as higher radiated and conducted emissions. Passive filters are used to ensure that the electromagnetic emissions are below the target limit values. During operation, losses in the filter components can lead to their maximum temperature being exceeded (<120°C). The project includes the design and optimization of these filters. Innovative, combined thermal-electrical processes are to be used to solve the current problem of thermal overload of EMC filters and prevent possible vehicle failures. During the course of the project, a digital representation of the system (Digital Twin) will be developed to investigate and predict the system behavior using data-based methods.
This project is conducted in cooperation with Valeo eAutomotive Germany GmbH and its EMC department in the Powertrain Systems division. The project is supported by Guido Rasek at Valeo.
In collaboration with POLIMI with Mrs. Professor Grassi Flavia.
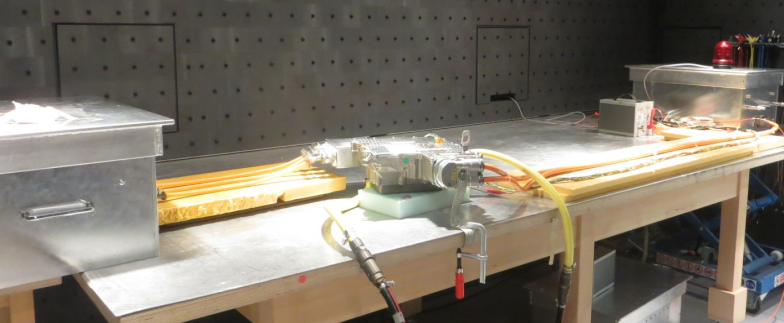
Measurement setup for EMC investigation of an electric power train. (Source: Valeo)
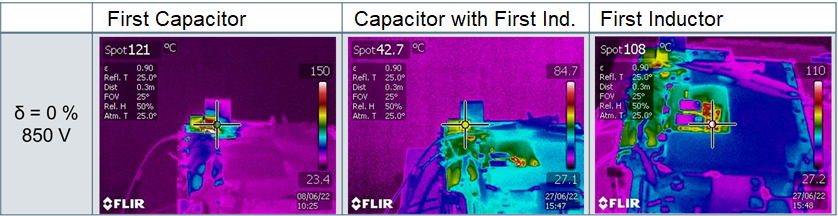
Heating of the filter caused by the dynamic disturbances in the drive train in different topologies. While the insertion of an inductor can lead to a reduction in the temperature at the first capacitor of the filter, this potentially leads to overheating of the inductor. (Source: Valeo)

